Supply and demand forex trading represents one of the most fundamental and powerful approaches to analyzing currency markets. Unlike complex technical indicators that often lag behind price action, supply and demand analysis focuses on the raw forces that actually move prices – the eternal battle between buyers and sellers in the forex market.
For new forex traders, understanding supply and demand concepts provides a solid foundation for making informed trading decisions. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about supply and demand forex trading, from basic concepts to advanced strategies used by professional traders.
Understanding Supply and Demand Forex Basics
What is Supply and Demand in Forex Trading?
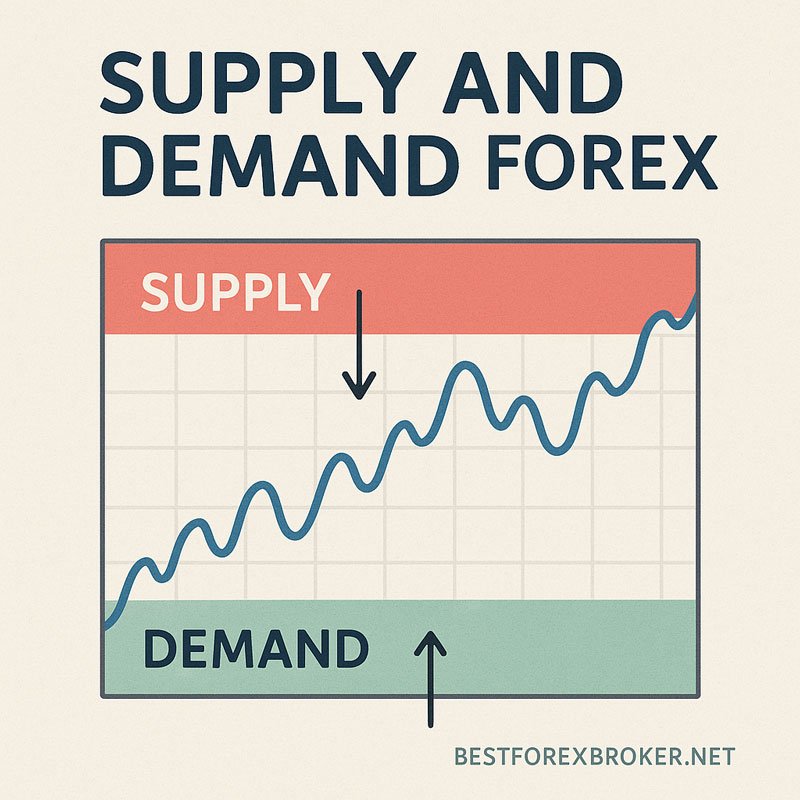
In forex markets, supply represents areas where selling pressure exceeds buying pressure, creating zones where prices tend to fall or stall. Conversely, demand represents areas where buying pressure exceeds selling pressure, forming zones where prices typically rise or find support.
These concepts mirror basic economic principles but apply directly to price charts. When institutional traders and market makers place large orders, they create imbalances that leave footprints on price charts – these footprints become our supply and demand zones.
Key Point: Unlike retail traders who can enter and exit positions quickly, institutional traders must break their large orders into smaller pieces, creating the price patterns we analyze.
The Psychology Behind Supply and Demand Zones
Understanding market psychology is crucial for successful supply and demand forex trading. When price approaches a supply zone, traders remember previous selling pressure at that level. This memory creates anticipation, often leading to self-fulfilling prophecies as traders position themselves for expected price movements.
Professional traders exploit this psychological tendency by identifying zones where institutional money previously entered the market, knowing that similar price reactions often occur when these levels are revisited.
Identifying Supply and Demand Zones in Forex Charts
Characteristics of Strong Supply Zones
Effective supply zone identification requires recognizing specific visual patterns on forex charts. Strong supply zones typically exhibit these characteristics:
- Sharp bearish moves away from resistance levels – indicating aggressive selling
- Low trading volume at the zone itself – suggesting limited buying interest
- Fresh zones that haven’t been tested multiple times – maintaining their effectiveness
- Clear rejection patterns such as long upper wicks or bearish engulfing candles
Recognizing Powerful Demand Zones
Demand zones show opposite characteristics to supply zones:
- Strong bullish moves away from support levels – demonstrating buying pressure
- Price rejection patterns like hammer candles or bullish pin bars
- Volume confirmation showing increased buying activity
- Multiple timeframe confluence where demand zones align across different timeframes
Tools and Techniques for Zone Identification
Professional supply and demand forex trading requires systematic zone identification. Use these proven techniques:
- Multiple Timeframe Analysis – Identify zones on higher timeframes (daily, 4-hour) for major levels, then use lower timeframes (1-hour, 15-minute) for precise entry points
- Price Action Patterns – Look for rally-base-rally (demand) and drop-base-drop (supply) formations
- Volume Analysis – Confirm zone strength with volume indicators where available
- Market Structure Analysis – Understand how zones fit within overall trend direction
Important Note: Never rely on a single timeframe for zone identification. Always confirm zones across multiple timeframes for higher probability trades.
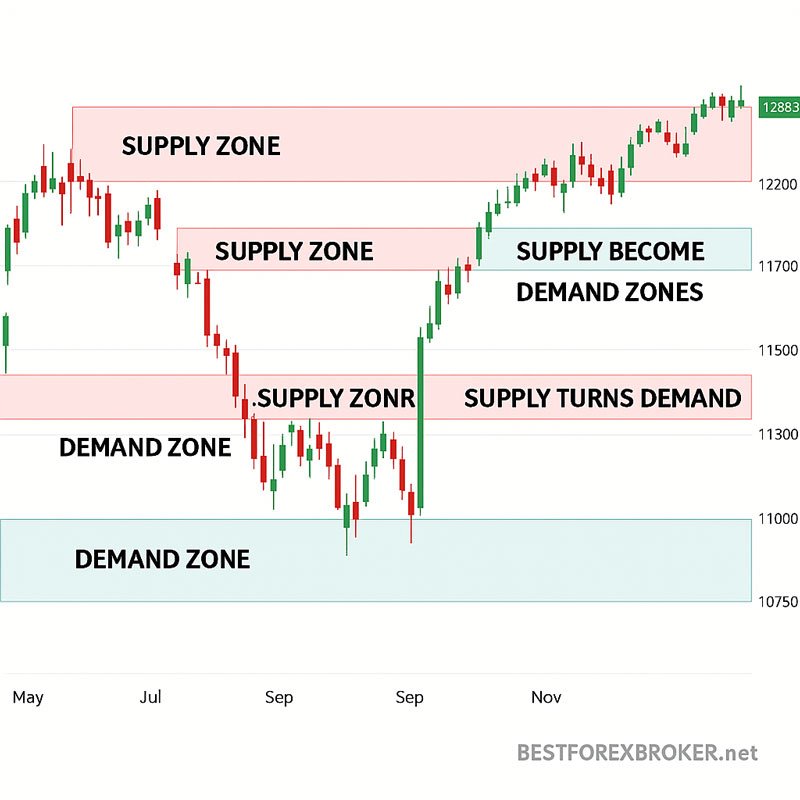
Types of Supply and Demand Zones
Fresh vs. Tested Zones
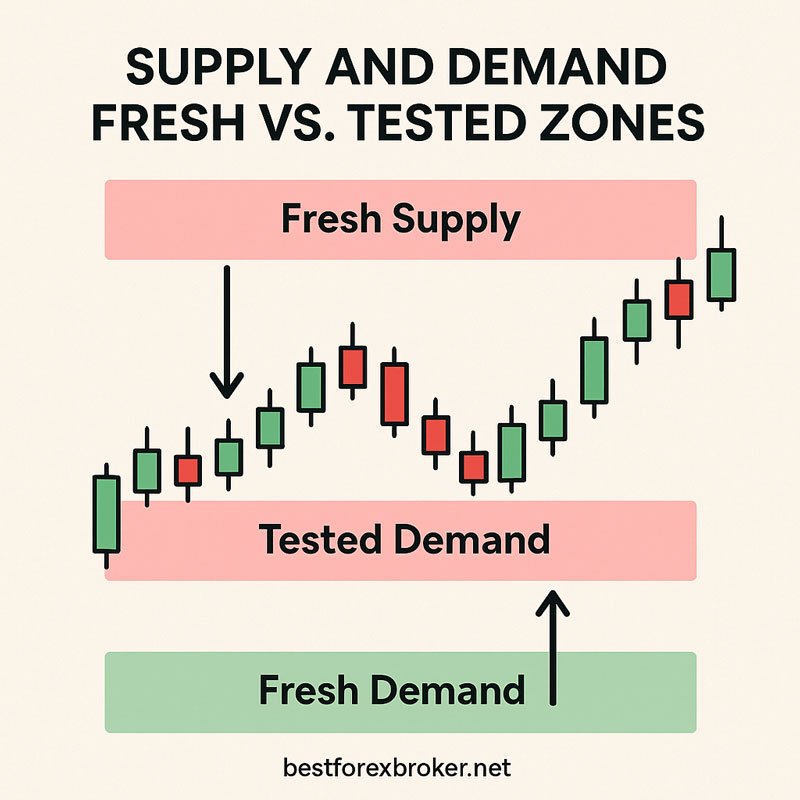
Fresh zones represent areas where price hasn’t returned since the initial strong move away. These zones typically offer the highest probability trades because the original orders may still be pending.
Tested zones have been touched by price one or more times. While they can still be effective, their strength diminishes with each test as orders get filled.
Proximal vs. Distal Zones
Proximal zones are close to current price action and more likely to be reached quickly. Distal zones are further from current price, offering potentially larger rewards but requiring more patience and stronger conviction.
Rally-Base-Rally and Drop-Base-Drop Patterns

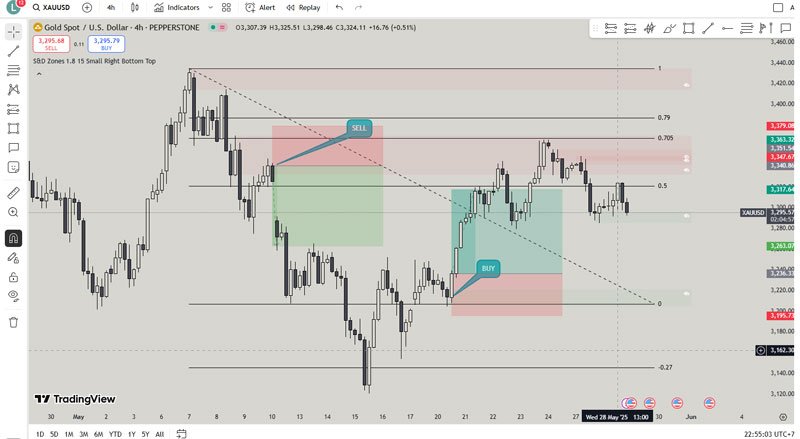
These patterns form the foundation of supply and demand forex trading:
- Rally-Base-Rally (RBR): Price rallies up, consolidates in a base, then rallies again – creating a demand zone
- Drop-Base-Drop (DBD): Price drops down, consolidates in a base, then drops again – forming a supply zone
These patterns indicate institutional accumulation or distribution, making them highly reliable for trading decisions.
Proven Supply and Demand Forex Trading Strategies
Entry Strategy Framework
Successful supply and demand forex trading requires disciplined entry strategies:
- Wait for Price to Return – Never chase price away from zones
- Seek Confirmation Signals – Look for reversal candlestick patterns or momentum divergence
- Consider Risk-Reward Ratios – Target minimum 1:2 risk-reward ratios, preferably 1:3 or higher
- Time Your Entry – Use lower timeframes for precise entry timing within the zone
Exit Strategy Best Practices
Professional exit strategies maximize profitability:
- Take Profits at Opposing Zones – Target the next significant supply or demand level
- Use Trailing Stops in Trending Markets – Capture additional profits when trades move favorably
- Manage Partial Positions – Close portions of profitable trades while letting winners run
Risk Management for Supply and Demand Trading
Effective risk management separates successful traders from unsuccessful ones:
- Position Size Based on Zone Strength – Risk more on fresh, confluent zones
- Strategic Stop Loss Placement – Place stops beyond the zone, not within it
- Maximum Risk Per Trade – Never risk more than 1-2% of account balance per trade
Critical Warning: Poor risk management destroys more trading accounts than incorrect market analysis. Always prioritize capital preservation.
Advanced Supply and Demand Concepts
Confluence Factors for Higher Probability Trades
Combining supply and demand with other analysis methods increases trade success rates:
- Fibonacci Retracements – Look for zones that align with key Fibonacci levels (38.2%, 50%, 61.8%)
- Trend Analysis – Trade demand zones in uptrends and supply zones in downtrends
- Economic News Events – Consider fundamental catalysts that might strengthen zone reactions
Market Structure Analysis Integration
Understanding market structure enhances supply and demand forex trading effectiveness:
- Uptrend Structure – Series of higher highs and higher lows, favor demand zones
- Downtrend Structure – Series of lower highs and lower lows, favor supply zones
- Break of Structure – Significant level breaks often signal trend changes
Multi-Timeframe Supply and Demand Approach
Professional traders always use multiple timeframes:
- Weekly/Daily Charts – Identify major supply and demand zones
- 4-Hour Charts – Refine zone boundaries and assess market structure
- 1-Hour/15-Minute Charts – Time precise entries and exits
This approach ensures alignment between short-term trades and longer-term market direction.
Common Mistakes in Supply and Demand Forex Trading
Over-Marking Charts with Zones
New traders often identify too many zones, cluttering charts and creating analysis paralysis. Focus on the most obvious, significant zones where strong moves originated.
Trading Weak or Old Zones
Avoid these low-probability zones:
- Zones tested multiple times
- Areas with gradual price moves rather than sharp reactions
- Zones from very small timeframes without higher timeframe confirmation
Ignoring Overall Market Sentiment
Supply and demand zones work best when aligned with broader market sentiment. Trading against strong fundamental trends significantly reduces success rates.
Poor Risk Management Practices
These mistakes destroy trading accounts:
- Risking too much per trade
- Moving stop losses against losing positions
- Failing to take profits at logical levels
Remember: Consistency beats home runs in forex trading. Focus on small, consistent gains rather than massive winners.
Practical Implementation Guide
Setting Up Your Charts for Success
Optimize your trading platform for supply and demand analysis:
- Use Clean Charts – Remove unnecessary indicators that create visual clutter
- Multiple Timeframe Layout – Display weekly, daily, 4-hour, and 1-hour charts simultaneously
- Mark Key Zones – Use horizontal lines or rectangles to clearly identify supply and demand areas
- Color Coding System – Use consistent colors (red for supply, blue for demand) across all timeframes
Developing Your Trading Plan
Create a systematic approach to supply and demand forex trading:
- Pre-Market Analysis – Identify key zones before trading sessions begin
- Entry Criteria Checklist – Define specific conditions that must be met before entering trades
- Trade Management Rules – Establish clear guidelines for position management
- Review and Improvement Process – Regularly analyze trades to identify areas for improvement
Tools and Resources for Supply and Demand Trading
Recommended Trading Platforms
Choose platforms that support effective supply and demand analysis:
- MetaTrader 4/5 with custom zone indicators
- TradingView for comprehensive charting capabilities
- Professional platforms like cTrader for advanced order management
Complementary Analysis Tools
These tools enhance supply and demand forex trading:
- Volume profile indicators (where available)
- Market structure indicators
- Multi-timeframe analysis tools
- Economic calendar integration
Building Long-Term Trading Success
Developing Expertise Through Practice
Supply and demand forex trading mastery requires consistent practice:
- Demo Trading – Practice zone identification and trade execution without financial risk
- Historical Chart Analysis – Study past price movements to improve pattern recognition
- Trade Journaling – Document every trade to identify strengths and weaknesses
- Continuous Education – Stay updated on market developments and refine your approach
Psychological Aspects of Trading
Successful trading requires mental discipline:
- Patience – Wait for high-probability setups rather than forcing trades
- Emotional Control – Avoid revenge trading after losses
- Consistency – Stick to your trading plan regardless of recent results
Professional Tip: Most trading failures result from psychological factors rather than technical inadequacy. Develop mental resilience alongside technical skills.
Conclusion
Supply and demand forex trading offers a powerful approach to understanding market dynamics and making profitable trading decisions. By focusing on areas where institutional money previously entered the market, traders can position themselves alongside the “smart money” rather than against it.
Success in supply and demand forex trading requires:
- Systematic zone identification across multiple timeframes
- Disciplined entry and exit strategies
- Robust risk management practices
- Continuous learning and adaptation
Remember that mastery takes time and practice. Start with demo trading to develop your skills without financial risk, then gradually transition to live trading as your competency improves. Focus on consistency over quick profits, and always prioritize capital preservation above all else.
The forex market will always present opportunities for prepared traders. By mastering supply and demand concepts and maintaining disciplined execution, you can join the ranks of successful currency traders who consistently profit from market movements.
This comprehensive guide provides the foundation for your supply and demand forex trading journey. Continue practicing, stay disciplined, and remember that successful trading is a marathon, not a sprint.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is supply and demand forex trading?
Supply and demand forex trading is a method that identifies areas on price charts where buying pressure (demand) or selling pressure (supply) previously caused significant price movements. Traders use these zones to predict future price reactions and make trading decisions.
How do you identify supply and demand zones in forex?
Identify supply and demand zones by looking for areas where price made sharp moves away from specific levels. Supply zones show strong bearish moves with selling pressure, while demand zones display strong bullish moves with buying pressure. Use multiple timeframes for confirmation.
Are supply and demand zones more effective than technical indicators?
Supply and demand zones can be more effective because they’re based on actual market participant behavior rather than mathematical calculations. However, combining zones with complementary analysis methods often produces the best results.
How long do supply and demand zones remain valid?
Zone validity depends on several factors including timeframe, number of tests, and market conditions. Fresh zones from higher timeframes typically remain valid longer than tested zones from lower timeframes. Generally, zones lose effectiveness after multiple touches.
What’s the best timeframe for supply and demand forex trading?
The best approach uses multiple timeframes: weekly/daily for major zones, 4-hour for market structure, and 1-hour/15-minute for precise entries. This multi-timeframe analysis provides comprehensive market perspective.
Can beginners successfully use supply and demand trading?
Yes, beginners can learn supply and demand trading, but it requires dedicated practice and proper education. Start with demo trading, focus on obvious zones, and always use proper risk management. Consistency and patience are crucial for success.